Coronary Artery Disease Robotic Surgery
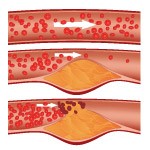
Coronary artery disease, also called coronary heart disease, is a common form of heart disease that occurs when the arteries that bring blood to the heart narrow or become clogged by plaque—a buildup of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. For severe cases, surgery is needed to widen or unblock clogged arteries to increase the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart.
Surgical Approaches
In traditional bypass surgery, doctors access the heart by making an 8- to 10-inch incision down the chest and opening the ribs—this is known as a sternotomy. Surgeons then take a segment of a healthy blood vessel from your chest, leg or arm and attach one end of that vessel to a healthy artery and the other end to the diseased coronary artery past the clogged area. This creates a new channel, allowing blood to flow freely again. A pump oxygenator—heart-lung machine—is used for many coronary bypass operations. It takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery.
The daVinci surgery for coronary artery disease is performed without the need for a heart-lung machine. It uses a minimally invasive approach with only small incisions between the ribs. This also avoids the need for a sternotomy.
Potential benefits include:
- Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery
- Less pain, scarring and risk of infection
- Significantly less blood loss and need for blood transfusions
- Quicker return to normal activities
- Significantly less risk of heart attack and stroke following surgery
- Superior results with less need for repeat surgery
- Significantly higher patient satisfaction

